Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer in men worldwide. According to international estimates about one in six men will get prostate cancer during their lifetime and worldwide, over 375,000 patients will die from it each year. Tumor resistance to current therapies plays an essential role in this and new approaches are therefore urgently needed.
Now an international research team from the University of Bern, Inselspital Bern and the University of Connecticut has identified a previously unknown weak spot in prostate cancer cells. This weak spot is possibly also present in other cancer cells. This could also lead to entirely new therapeutic approaches for other types of cancer.
The study was led by UConn molecular developmental biologist Rahul Kanadia from the Department of Physiology and Neurobiology and the Institute for Systems Genomics, and Mark Rubin from the Department for Biomedical Research (DBMR) and Center for Precision Medicine (BCPM) at the University of Bern and Inselspital Bern. The research results have now been published in the journal Molecular Cell.
Previously unknown driver of prostate cancer identified
“We took a closer look at a certain molecular machine called the spliceosome,” explains Anke Augspach, lead author of the study and researcher from the Department for BioMedical Research (DBMR). “It plays an important role in the translation of genes into proteins. In this process, the spliceosome separates parts of the gene that are not needed for the production of the protein and fuses the other parts.”
While almost all genes undergo this process in the so-called major spliceosome, the minor spliceosome is used in less than one percent of genes.
“Nevertheless, the minor spliceosome is enormously important because it particularly processes genes that play a crucial role in cell growth. And it is this cell growth that gets out of control in cancer – but the precise mechanism behind this remained unclear,” explains Kanadia. In their investigations, the team found various indications for the central role of the minor spliceosome in cancer.
“We were able to show that a specific component of the minor spliceosome is significantly increased in advanced prostate cancer,” explains Rubin. This led the researchers to suspect that cancer cells activate the minor spliceosome through this component and thus stimulate uncontrolled cell growth.
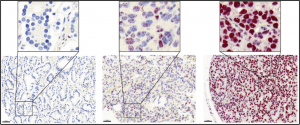
The researchers were able to confirm their assumption with the help of laboratory test models such as 2D cell cultures and organoids – miniature organs that are grown in the laboratory based on patient samples. They were also able to show that inhibiting the specific component led to a greater reduction in the growth of prostate cancer than current standard therapies.
“Accordingly, blocking this process should hold therapeutic potential,” Rubin says. “This is the target that that we were hunting.”
Kanadia adds that “the blocking leads to a decrease in cancer growth without affecting the growth and survival of normal cells.”
“This discovery is a game changer in developing more effective and targeted combination therapies for cancers such as prostate cancer and other types of cancer. We want to work on this in the coming years – and have already applied for the corresponding patent,” Rubin concludes.
The research results come from a project supported by the US Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF) with the Igor Tulchinsky-Leerom Segal-PCF Challenge Award 2022. The foundation funds interdisciplinary projects that pursue promising approaches to combat recurrent or advanced prostate cancer. The award is endowed with $1 million.
“We commend the research team on their achievement and proudly support their work to bring us closer to our mission to eliminate death and suffering from prostate cancer,” says Howard R. Soule, Executive Vice President and Chief Science Officer of the PCF.



