Writer
Kim Krieger
Kim Krieger has covered politics from Capitol Hill and energy commodities from the floor of the New York Mercantile Exchange. Her stories have exposed fraud in the California power markets and mathematical malfeasance in physics. And she knows what really goes on in the National Radio Quiet Zone. These days, Kim tells clear, compelling stories of the research at UConn. Her work connects Connecticut citizens and the press with the vast resources of their flagship public university. When not at UConn, she can be found kayaking among the beautiful Norwalk islands, digging in her garden, or occasionally enjoying the silence in the National Radio Quiet Zone.
Author Archive
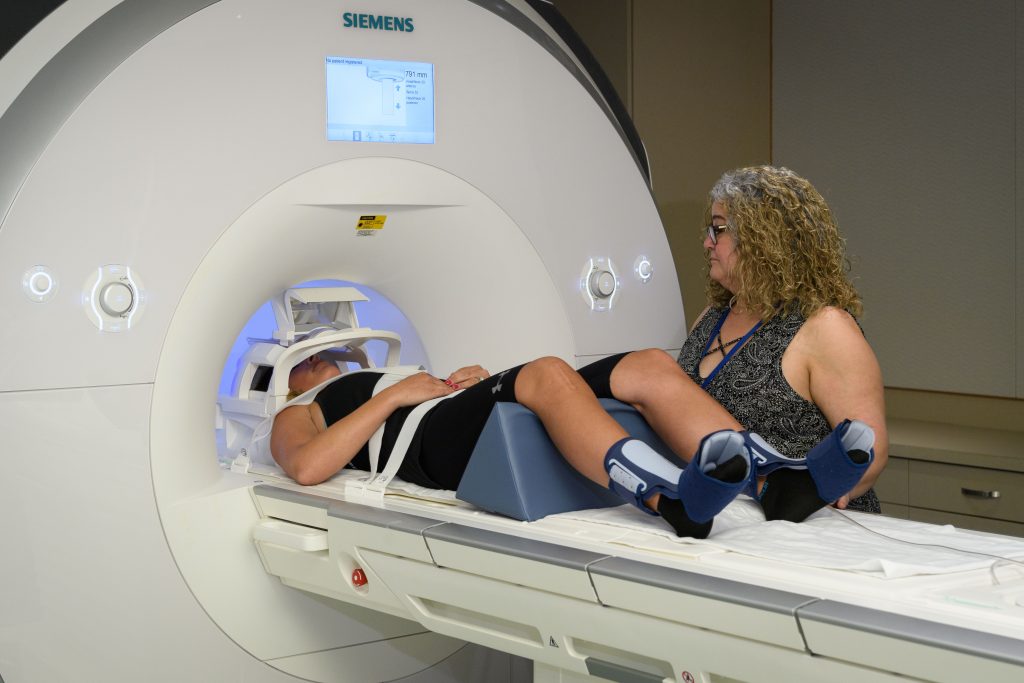
UConn Health Patients Can Now Get MRIs at UConn in Storrs
Thanks to a collaboration between UConn Health physicians and UConn researchers, sophisticated MRI scanning equipment originally purchased for research use will now be used for diagnosing patients of UConn Health in Storrs.
November 29, 2018 | Kim Krieger
Curators Versus Cancer
A special team of medical literature experts are on the hunt for cancer's kryptonite, one mutation at a time.
November 27, 2018 | Kim Krieger
Moving the Motivation Meter
UConn researchers led by behavioral neuroscientist John Salamone have found that two experimental drugs boost motivation in rats, pointing the way to potential treatments.
November 8, 2018 | Kim Krieger
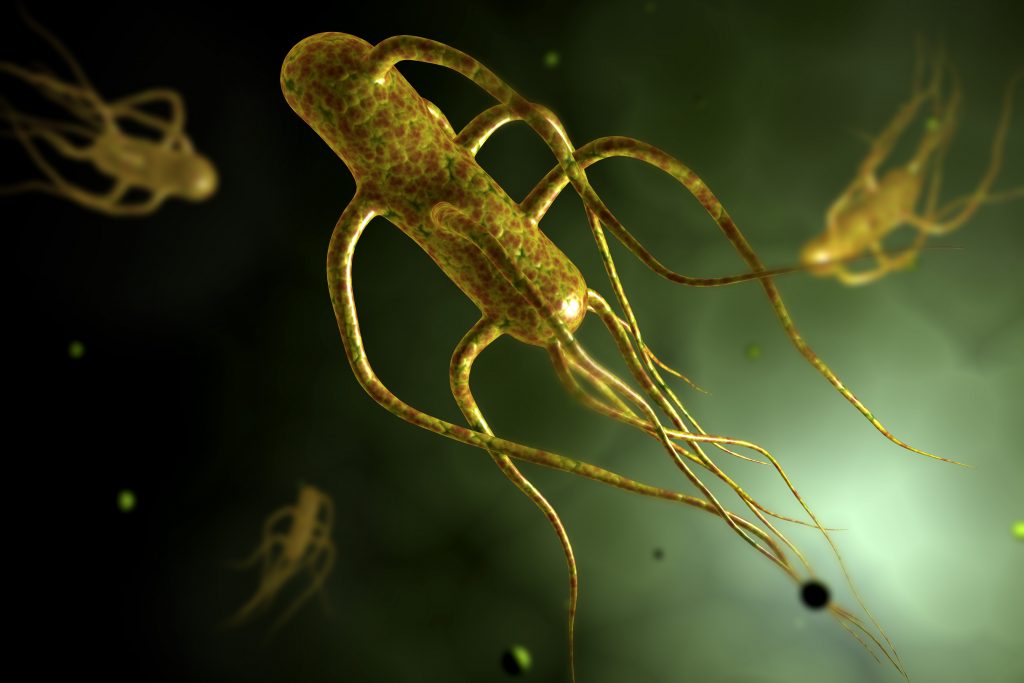
T Cells That Stay Put Could Be Key to a Better Salmonella Vaccine
UConn and UC Davis researchers announced a breakthrough in understanding which cells protect against Salmonella – a critical step in developing a better vaccine against the often deadly bacterium.
November 7, 2018 | Kim Krieger
The Blitz of Neuroscience
UConn neuroscience researchers from across departments and campuses came together this week for a "datablitz," where several graduate students presented fast-moving summaries of their research to a live audience.
October 30, 2018 | Kim Krieger
Suicide Risk Higher Among Older Vets Who Were in Jail
Veterans released from prison are five times as likely to attempt suicide as their peers who have never been incarcerated, according to a study by UConn Health researchers.
October 29, 2018 | Kim Krieger
Old Drug, New Hope for Pediatric Brain Cancer
Researchers from JAX, Connecticut Children's Hospital, and UConn Health have identified several drugs used against other diseases that also have the potential to fight the most common form of childhood brain cancer.
October 25, 2018 | Kim Krieger
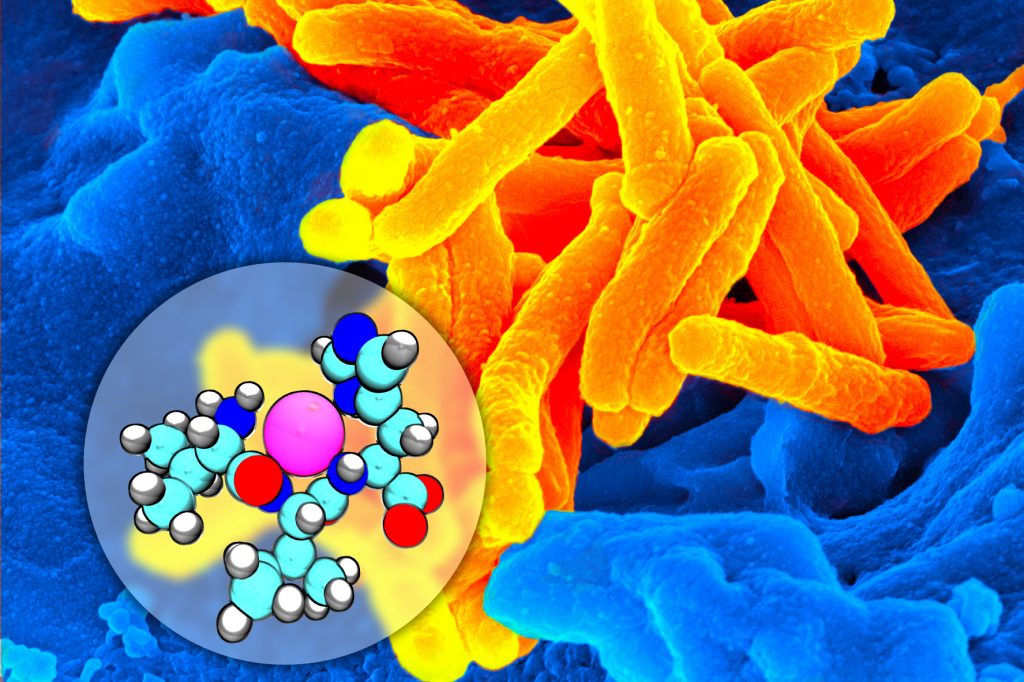
A Copper Bullet for Tuberculosis
In a new study, UConn chemists report a new antibiotic that can find and kill tuberculosis bacteria where they hide.
October 23, 2018 | Kim Krieger
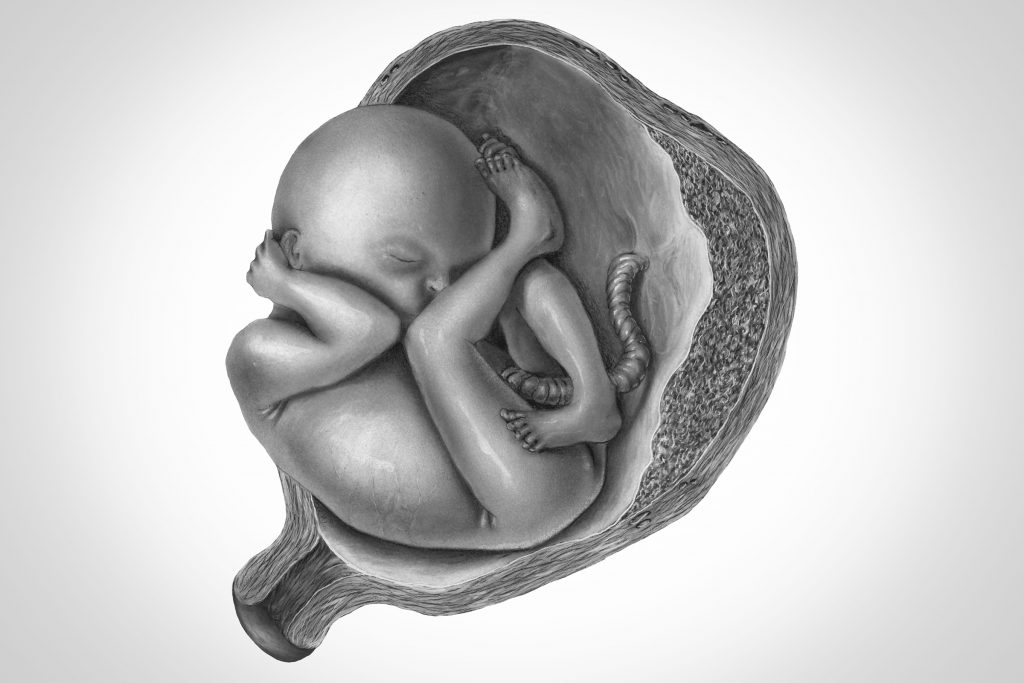
Calm the Immune System, Halt Premature Birth
UConn Health researchers found that a drug that blocks the cytokine GM-CSF may reduce the number of preterm births.
October 12, 2018 | Kim Krieger
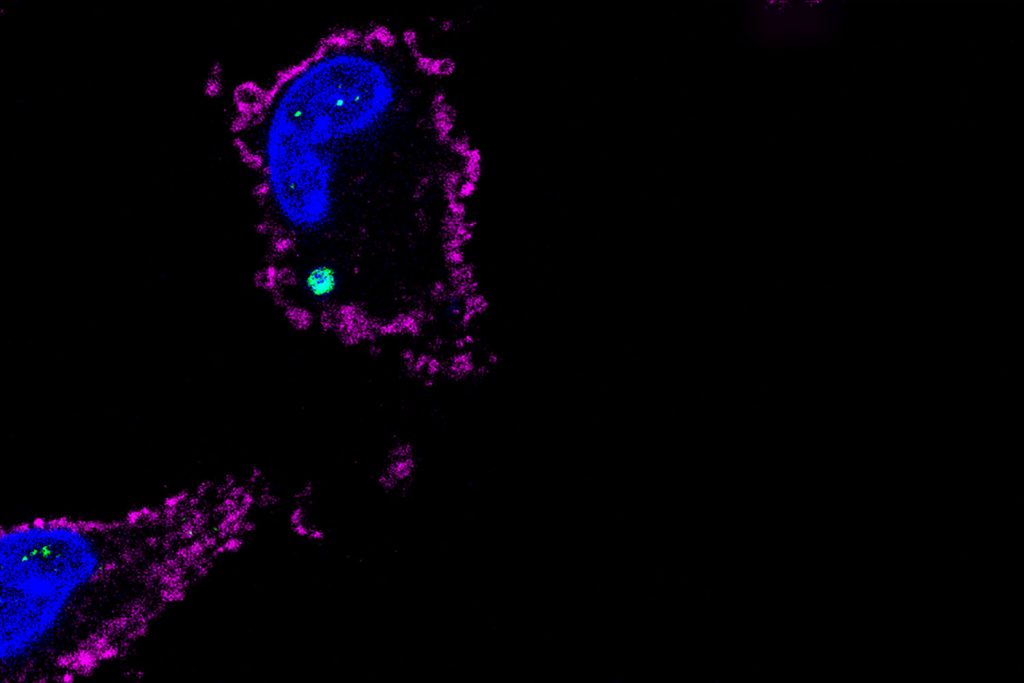
Cell Death Protein also Damps Inflammation
A new study by UConn Health researchers shows how the body keeps inflammation in check, making double use of a protein previously thought to be responsible only for cell death.
October 1, 2018 | Kim Krieger