Health & Well-Being
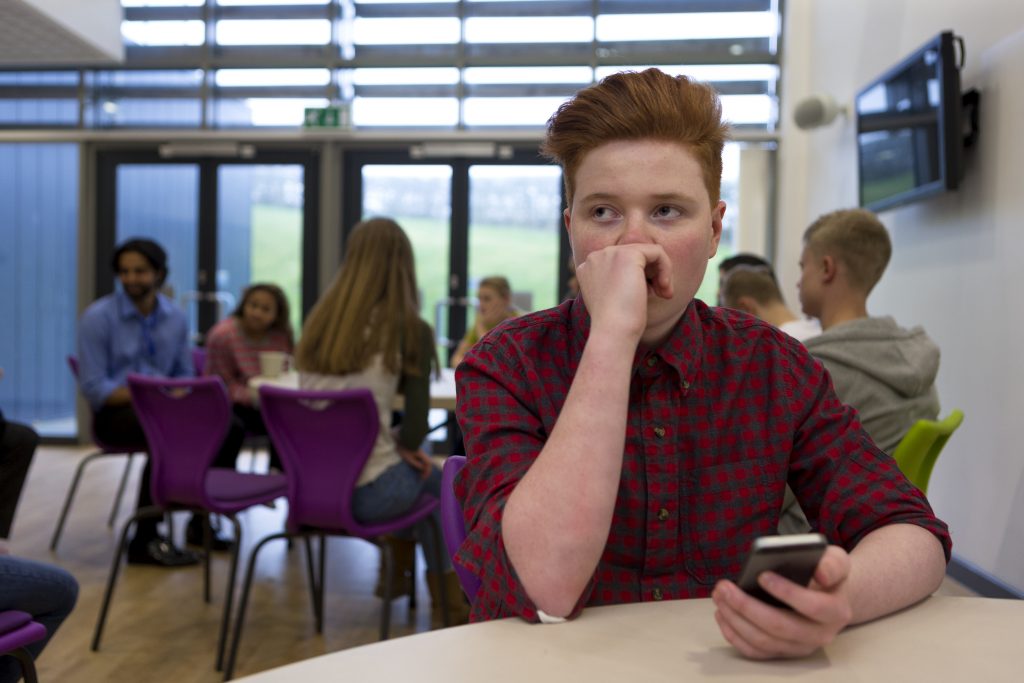
LGBTQ Teens Face High Rate of Weight-Based Bullying
As many as 44 percent of LGBTQ teens report weight-based bullying from both peers and family members, says a new UConn study.
February 7, 2019 | Combined Reports
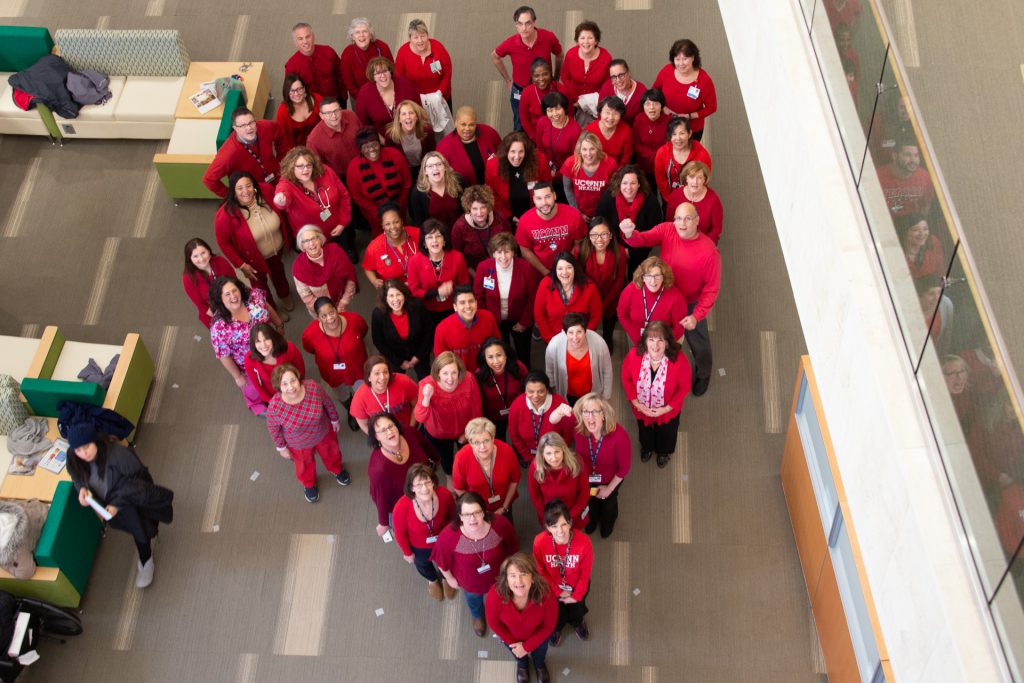
UConn Health Goes Red for Women’s Heart Health
Staff at UConn Health wore a piece of red clothing on Friday, National Wear Red Day, to raise awareness about the importance of preventing heart disease and stroke in women.
February 1, 2019 | Tina Encarnacion
Artificial Skin Could Give Superhuman Perception
Metal skin might sound like a superhero power, but UConn researchers hope it could help burn victims 'feel' again.
January 22, 2019 | Kim Krieger
Meet the Researchers: Spirochete Labs
Anyone who has had to move knows what a pain it is. But imagine not just moving geographically, but switching between completely different biological environments with different nutrients available and immune systems working against you – well that’s the life cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi the bacteria that causes Lyme disease. The most prevalent arthropod-borne infection […]
January 22, 2019 | Anna Zarra Aldrich '20 (CLAS), Office of the Vice President for Research
Common Gene Disorder that Causes Serious ‘Stealth’ Disease Could be Easily Treated
Routine screening may be needed for people at risk of hemochromatosis, according to research by UConn Health and University of Exeter.
January 16, 2019 | UConn Health and University of Exeter
Looking to the Day When Being a Woman in STEM Won’t Be an Issue
Pain researcher Erin Young can't wait for people to stop asking what it's like to be a woman in her field.
January 16, 2019 | Julie (Stagis) Bartucca '10 (BUS, CLAS), '19 MBA
Food Ads Target Black and Hispanic Youth with Unhealthy Products
Black children and teens each viewed an average of more than 16 food-related ads per day in 2017, compared to 8.8 ads-per-day for white children and 7.8 ads for white teens.
January 15, 2019 | Combined Reports
Health Disparities Damage Men and Boys of Color and CT’s Economy
Commenting on a recently published report by the Health Disparities Institute at UConn Health, its director says addressing health equity is not just a matter of social justice but, for Connecticut, may be a matter of economic survival.
January 14, 2019 | Kim Krieger
Hearing Loss Announced by Protein Boom in Blood
After finding that blood levels of a special protein found only in the inner ear spike after exposure to loud noise, UConn Health researchers are developing tests to identify those at risk of hearing loss.
January 7, 2019 | Kim Krieger
Susan Brillhart ’84 (NUR), A Voice for the Most Vulnerable
Hers is a voice for the most vulnerable among us.
January 4, 2019 | Jackie Hennessey ’83 (CLAS)