Undergraduates
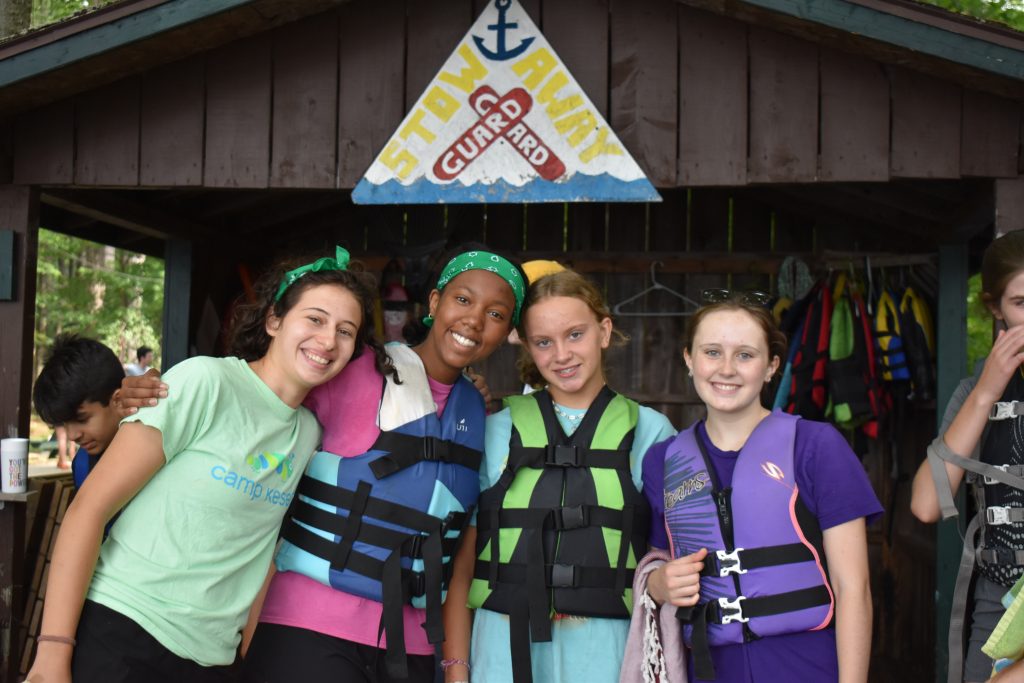
Kesem: Camp, Care, and Connections for Kids Impacted by a Parent’s Cancer
Camp Kesem UConn is gearing up to host its third summer camp to support children whose caregivers have cancer
December 21, 2023 | Mac Murray
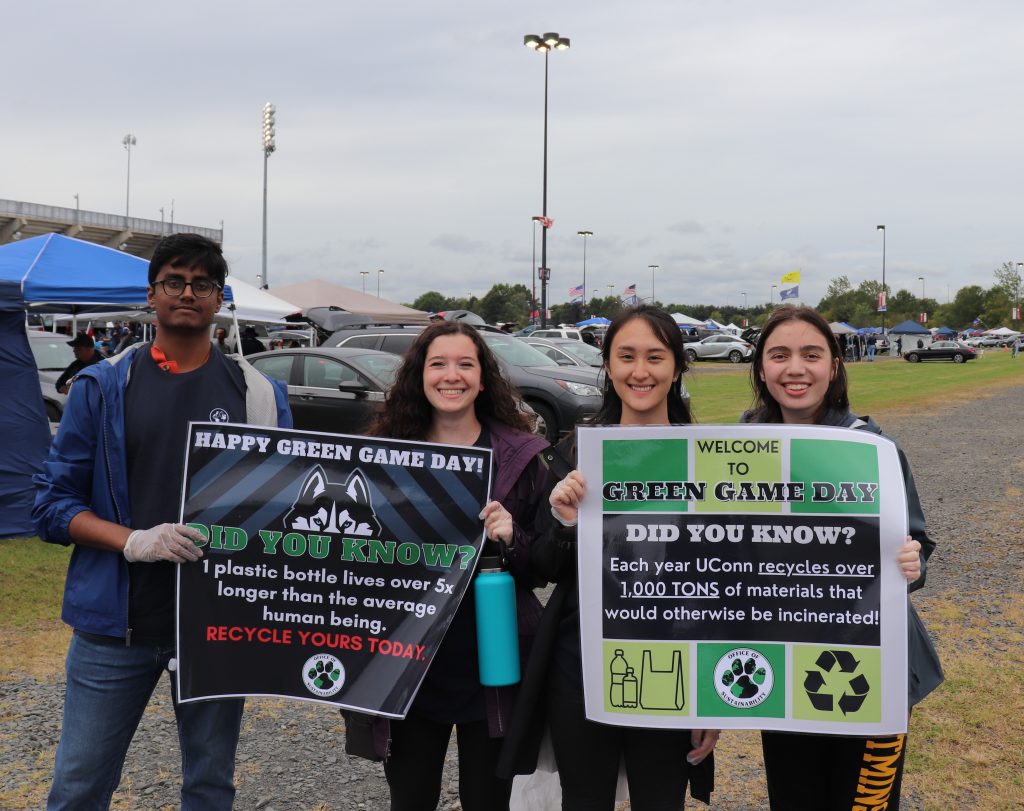
UConn Earns High Marks in Global Sustainable University Ratings
GreenMetric releases global higher education sustainability rankings for 2023
December 12, 2023 | Betsy Mortensen and Amanda McCard '25 (CLAS), Office of Sustainability
Students Cite Academic Support, Advising, On-Campus Housing as Top Priorities
Student survey provides insight to University's new strategic plan
December 5, 2023 | Stephanie Reitz - UConn Communications
After Semester-Long Development, Student-Created ‘BrewConn’ Beer Debuts with Glowing Reviews
New UConn brewing innovation initiative seeks to bring education, research, outreach to industry
November 30, 2023 | Claire Hall
UConn MSE Sweeps the 2023 ASM International Materials Challenges
UConn MSE undergraduate students placed first in two different materials challenges and MSE PhD student placed 3rd at the annual IMAT – Heat Treat conference
November 16, 2023 | Alec Arbia, Written Communications Assistant, Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Month of Discovery Student Researcher: Aria Penna, BUS ‘25
Aria Penna's transformative journey at UConn, from a law school hopeful to a budding entrepreneur and finance enthusiast. This story is part of the Month of Discovery series
October 31, 2023 | Christie Wang. for UConn Research
UConn Student’s Trans Photography Project Has One Simple Goal – To Affirm
'It’s a personal mission of mine to make sure that trans people have photos of themselves that make them feel proud and happy'
October 30, 2023 | Kimberly Phillips
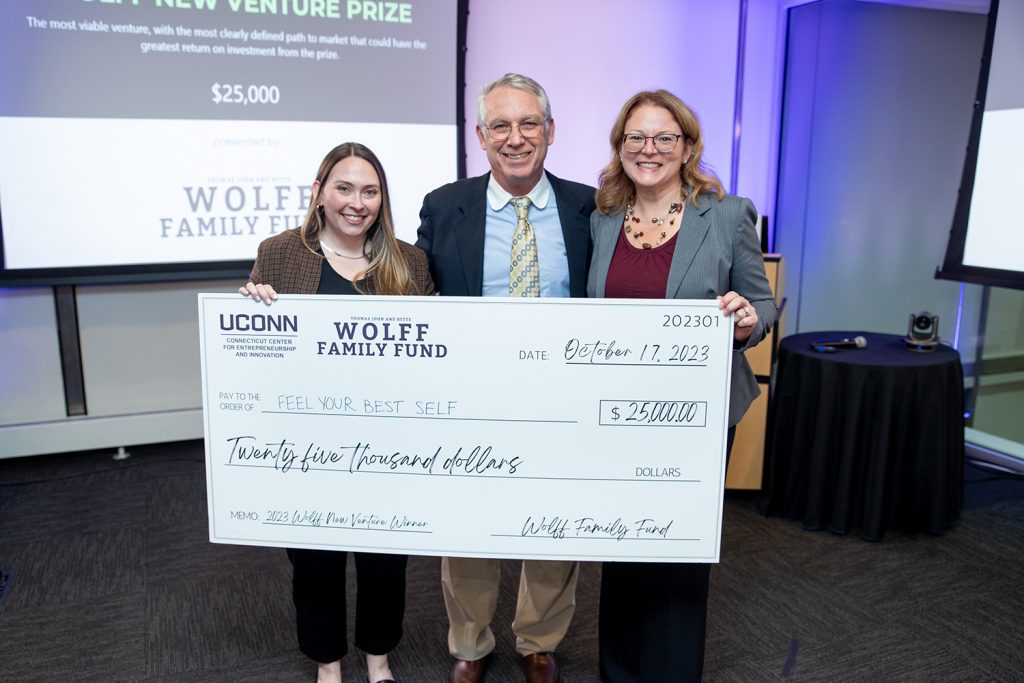
Wolff Entrepreneurship Competition Crowns Startup That Brings Emotional-Coping Skills to Elementary-Age Kids
The Wolff competition awarded almost $60,000 in funds for UConn-affiliated startups
October 20, 2023 | Claire Hall
Marketing Students Played a Pivotal Role in Creating a Safer UConn
'I knew it could save lives'
October 17, 2023 | Claire Hall
Finance Major Was Part of Fulbright U.K. Summer Institute
Chapal Bhavsar was selected to be part of an interdisciplinary program emphasizing climate change, sustainability, and civic responsibility for the future of the planet
October 16, 2023 | Mike Enright '88 (CLAS), University Communications