Health & Well-Being
Food Ads Target Black and Hispanic Youth with Unhealthy Products
Black children and teens each viewed an average of more than 16 food-related ads per day in 2017, compared to 8.8 ads-per-day for white children and 7.8 ads for white teens.
January 15, 2019 | Combined Reports
Health Disparities Damage Men and Boys of Color and CT’s Economy
Commenting on a recently published report by the Health Disparities Institute at UConn Health, its director says addressing health equity is not just a matter of social justice but, for Connecticut, may be a matter of economic survival.
January 14, 2019 | Kim Krieger
Hearing Loss Announced by Protein Boom in Blood
After finding that blood levels of a special protein found only in the inner ear spike after exposure to loud noise, UConn Health researchers are developing tests to identify those at risk of hearing loss.
January 7, 2019 | Kim Krieger
Susan Brillhart ’84 (NUR), A Voice for the Most Vulnerable
Hers is a voice for the most vulnerable among us.
January 4, 2019 | Jackie Hennessey ’83 (CLAS)
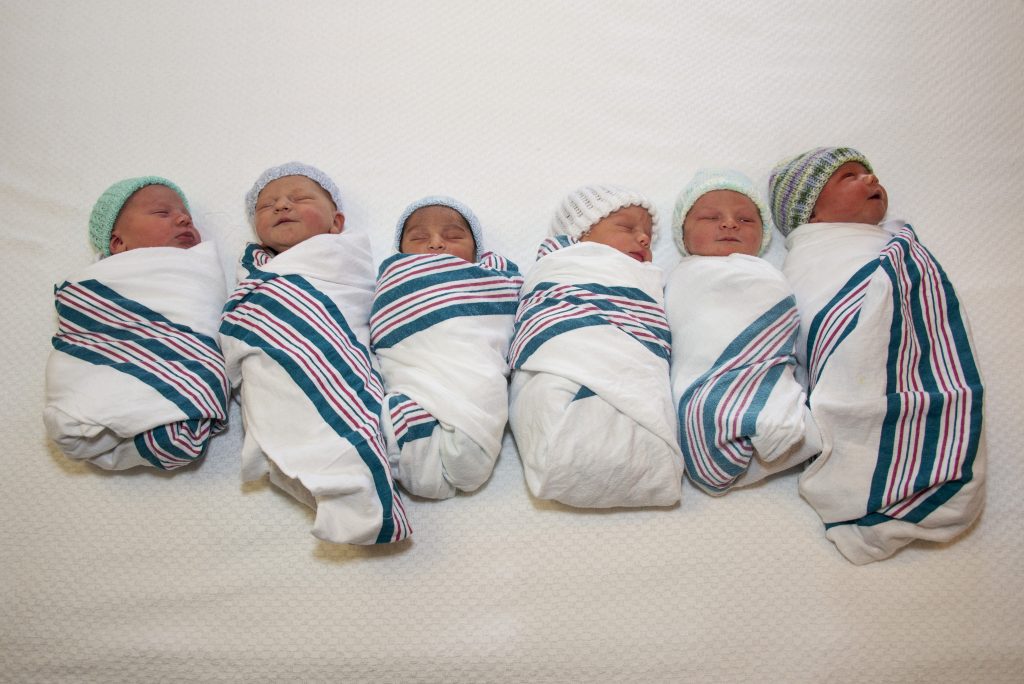
Six New Year’s Babies Set Record at UConn John Dempsey Hospital
It's a boy! No, wait ... it's a girl, boy, boy, girl, boy. The half-dozen New Year's Day babies set a record for UConn's hospital.
January 3, 2019 | Delker Vardilos, UConn Health
Beware of Natural Supplements for Sex Gain and Weight Loss
A pharmacy professor writes about his concerns that many so-called natural products are tainted with prescription drugs, thereby increasing the risk of harm to patients.
December 18, 2018 | C. Michael White, Department of Pharmacy Practice
School-Based Nutritional Programs Reduce Student Obesity
Implementing strong school nutrition policies is associated with healthier weight gain in middle school students, according to a new study by researchers at UConn and Yale.
December 17, 2018 | Kristin Messina, UConn Rudd Center
Nature is a Rich Source of Medicine – If We Can Protect It
Conservative estimates suggest that we are losing one important drug every two years because of our onslaught on the natural world, according to UConn's John Malone and counterparts.
December 13, 2018 | John Malone, UConn; Ross Piper, University of Leeds; Alexander Kagansky, University of Edinburgh; Nils Bunnefeld, University of Stirling; Rob Jenkins, University of York.
UConn Research Project at the International Space Station
An experiment devised by researchers at UConn startup LambdaVision was launched into space this month.
December 4, 2018 | Jessica McBride, PhD
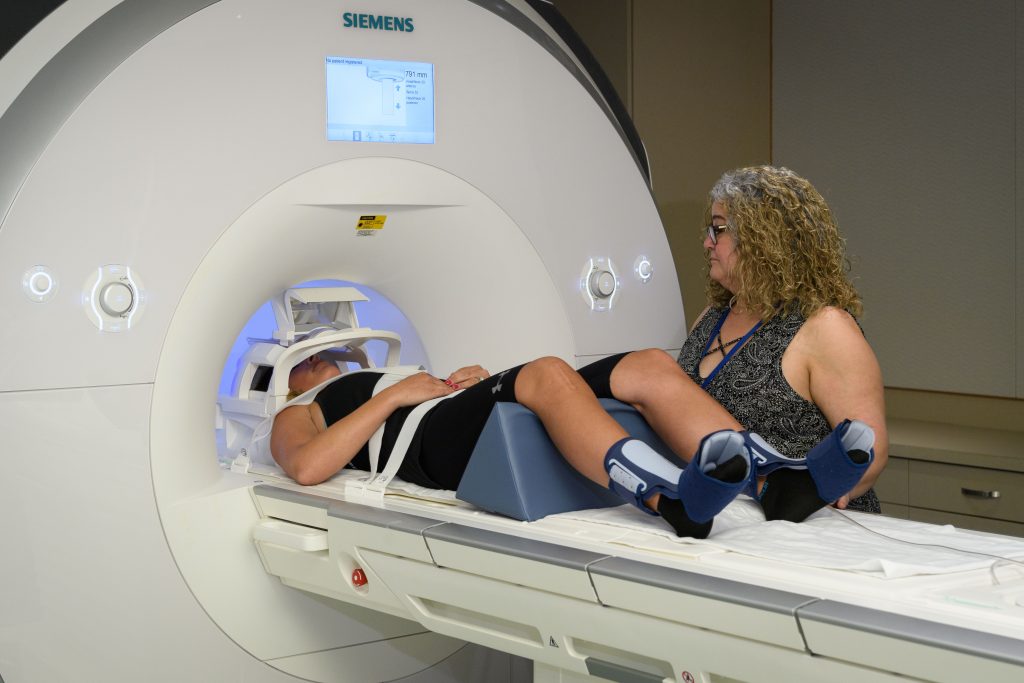
UConn Health Patients Can Now Get MRIs at UConn in Storrs
Thanks to a collaboration between UConn Health physicians and UConn researchers, sophisticated MRI scanning equipment originally purchased for research use will now be used for diagnosing patients of UConn Health in Storrs.
November 29, 2018 | Kim Krieger