Health & Well-Being
Study of COVID-19 Risk Communication Finds ‘Optimistic Bias’ Slows Preventive Behavior
A study has found that "optimistic bias" can hinder individuals' efforts to take precautions in the face of health threats like the coronavirus pandemic.
April 8, 2020 | Kenneth Best
COVID-19 Testing Available To UConn Students In Storrs
UConn students can now be tested for the COVID-19 virus on the Storrs campus in a familiar and friendly location through Student Health and Wellness (SHaW).
April 7, 2020 | Mike Enright '88 (CLAS), University Communications
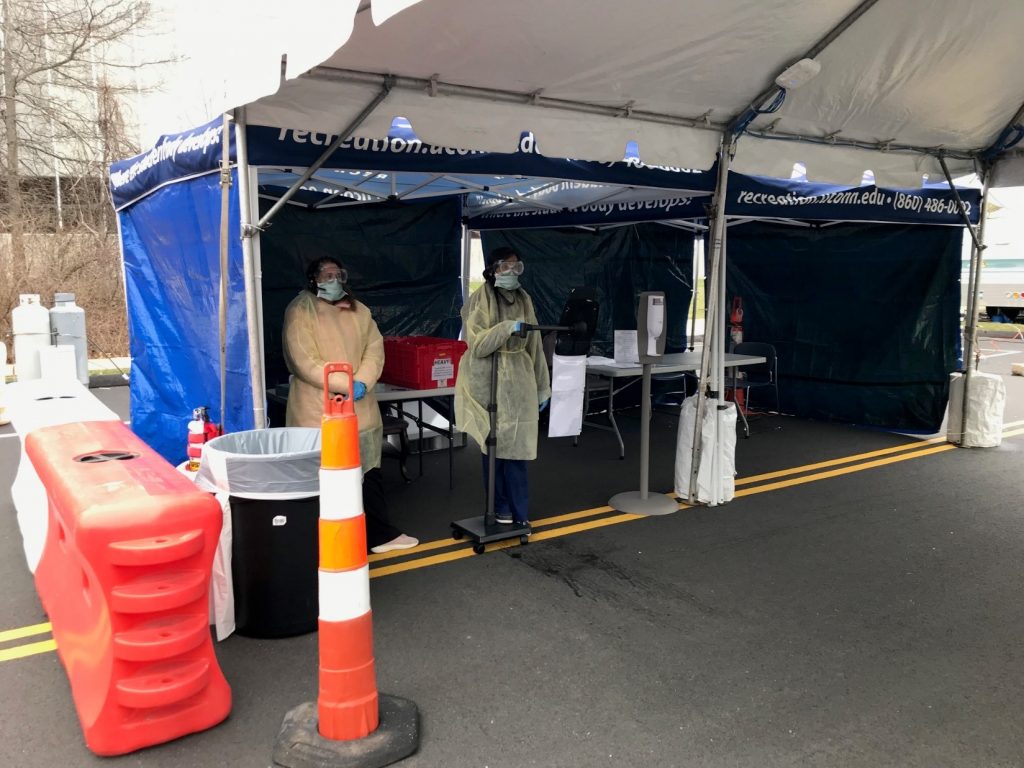
UConn Health Testing Site Setup Was An All-Hands-On-Deck Effort
The efficiency of the testing site is the result of hours of planning and preparation by the entire staff at UConn Health.
April 6, 2020 | Mike Enright '88 (CLAS), University Communications
Q&A: Pregnancy in a Pandemic
UConn Health's Dr. Christopher Morosky answers questions about pregnancy and COVID-19.
April 6, 2020 | Jaclyn Severance
Care for the Caregiver in the Age of Coronavirus
UConn Health's Dr. Karina Berg discusses how to care for someone at home with coronavirus - and how caregivers should maintain their own health.
April 2, 2020 | Chris DeFrancesco '94 (CLAS)
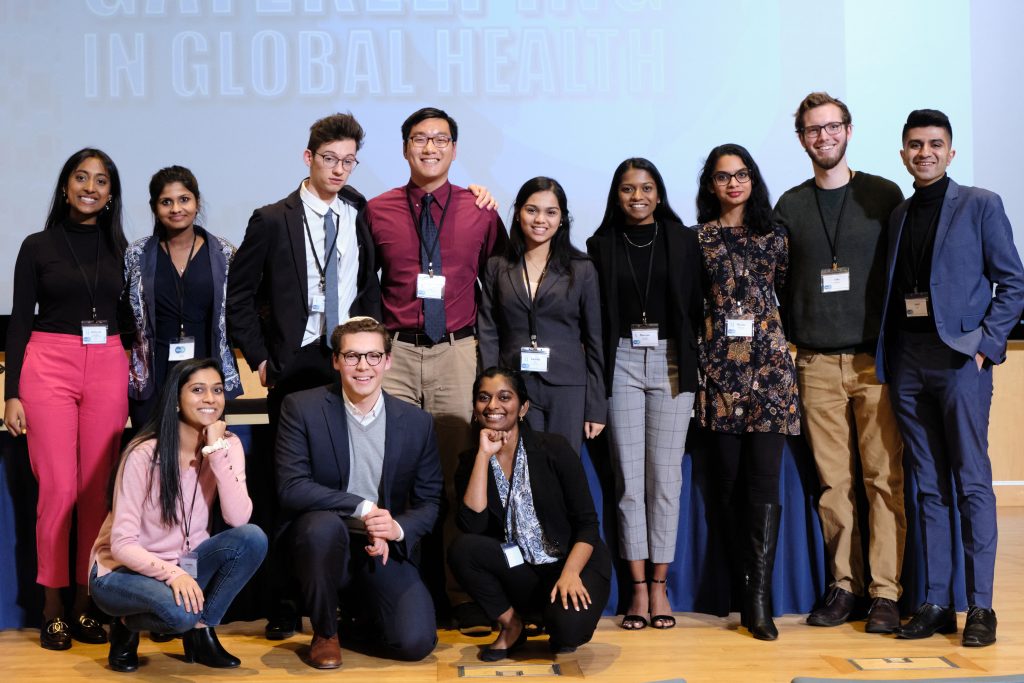
Gatekeeping in Global Health – A Student Organized Global Health Symposium on Health Disparities
Amidst a global pandemic, it is difficult to remember a time when we were not all thinking about global health issues. For Global Health Spaces on Campus (GloHSOC), the need to build enduring proactive, community-centered health care systems have always been at the forefront long before we arrived at our current state.
April 1, 2020 | Sahil Laul
Farmington and Storrs Team to Make Needed PPE for UConn Health
The collaborative efforts of medical doctors from UConn Health with engineers, scientists, and researchers from Storrs will soon produce an increased supply of personal protection equipment,
April 1, 2020 | Mike Enright '88 (CLAS), University Communications
Yearlong UConn Study to Look at COVID-19, Pandemic Preventative Health Behavior
UConn researcher Natalie J. Shook has received funding to study how people respond to recommended behaviors during health crises like COVID-19.
March 31, 2020 | Jaclyn Severance
Happy National Doctors’ Day
We are so proud of the selflessness, courage, kindness, and competence of our doctors, nurses and other healthcare workers who are battling COVID-19.
March 30, 2020 | Combined Reports
How You Can Help UConn Health Fight Coronavirus
UConn Health has been overwhelmed by the generosity of people seeking to help frontline workers in the battle against COVID-19. Here's how you can help.
March 26, 2020 | Combined Reports