Research & Discovery
UConn Puts Seven On List Of World’s Most Highly-Cited Researchers
Six UConn faculty members were named to a list of researchers with significant influence in their fields.
November 22, 2019 | Mike Enright '88 (CLAS), University Communications
Nature Features Brain Cancer Research From UConn Health, JAX
Two UConn medical students join UConn Health’s neurosurgery chief among a worldwide research collaborative reporting progress toward a better understanding of the behavior of certain brain tumor cells, and ultimately, better treatments and prognoses.
November 21, 2019 | Chris DeFrancesco '94 (CLAS) - UConn Health
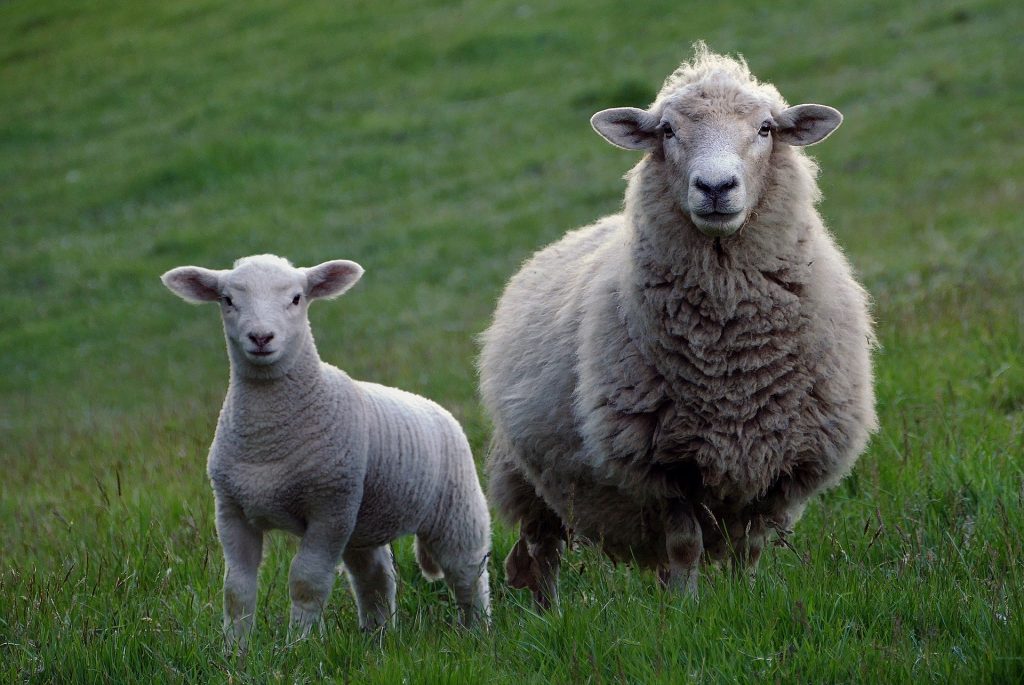
Maternal Nutrition Across Generations of Livestock
UConn researchers will try to identify mechanisms that alter growth and efficiency across multiple generations of livestock, thanks to a new grant from the USDA.
November 21, 2019 | Samantha Korittke '21 (CLAS), Office of the Vice President for Research
Turning on Silenced Genes in Prader-Willi Research
A UConn Health research team has received nearly $3 million from the NIH to investigate the molecular underpinnings of Prader-Willi syndrome, a rare neurogenetic disorder.
November 20, 2019 | Anna Zarra Aldrich '20 (CLAS), Office of the Vice President for Research
Turning to Old Remedies For New Health Challenges
UConn researchers are experimenting with old approaches to solve a growing problem: potentially deadly pathogens that are resistant to antibiotics.
November 19, 2019 | Elaina Hancock - UConn Communications
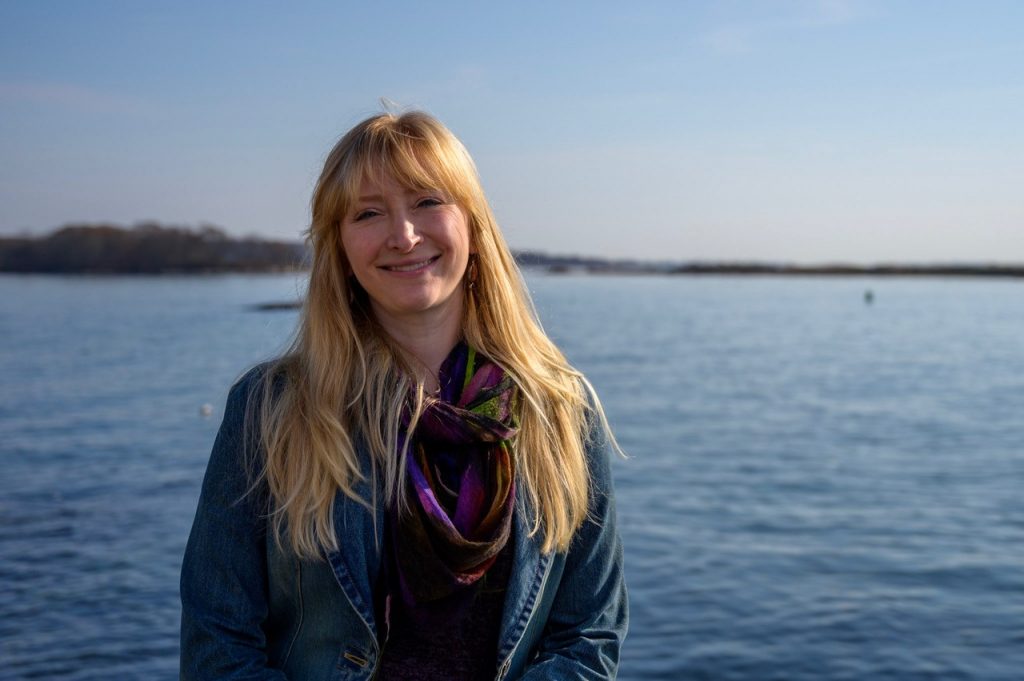
Meet the Researcher: Samantha Siedlecki, Marine Sciences
Samantha Siedlecki spearheads research on coastal environments, and is currently developing a regional model of ocean acidification for the East Coast.
November 18, 2019 | Anna Zarra Aldrich '20 (CLAS), Office of the Vice President for Research
Not Only Adorable: Squid Open Up New Antimicrobial Drug Possibilities
The glowing Hawaiian bobtail squid is more than a pretty face: New research shows that its symbiotic bacteria create antifungal compounds, which may be of use in drug discovery.
November 15, 2019 | Christine Buckley - College of Liberal Arts and Sciences
Breaking CO2 faster, cheaper, and more efficiently
A new discovery could make it possible to economically turn carbon dioxide into fuels.
November 15, 2019 | Kim Krieger - UConn Communications
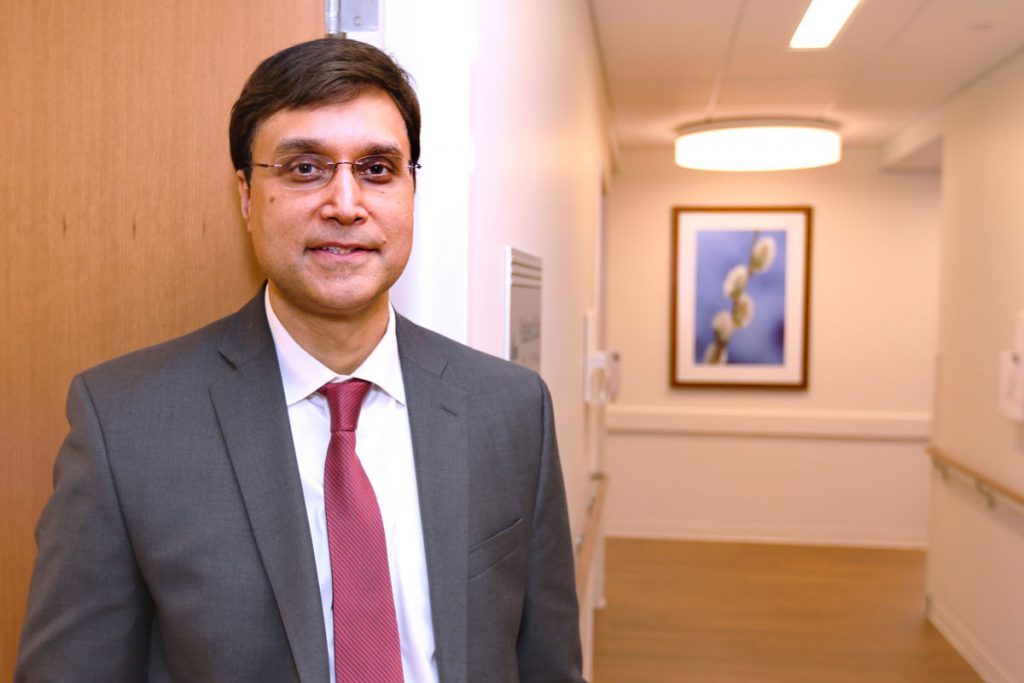
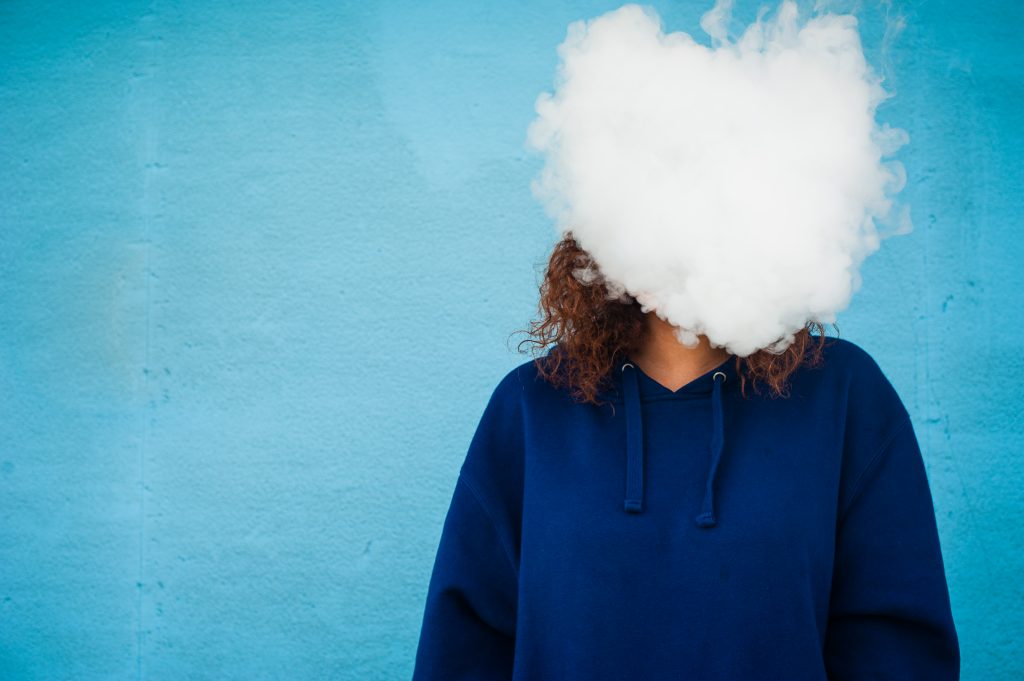
Q&A: The Dangers of Vaping
UConn Health’s Dr. Mario F Perez, assistant professor of medicine at UConn School of Medicine, discusses his research pointing to potential dangers associated with vaping.
November 14, 2019 | Lauren Woods - UConn School of Medicine
The Heart of the Matter: Genome Editing for Cardiovascular Diseases
Joint researcher from UConn Health and JAX, J. Travis Hinson's $3M grant is a pivotal step toward realizing the promise of genome editing and human precision medicine of cardiovascular and other disorders.
November 13, 2019 | Anna Zarra Aldrich '20 (CLAS), Office of the Vice President for Research